SpringAOP简介
面向切面编程(Aspect Oriented Programming)提供了另一种角度来思考程序的结构,通过这种方式弥补面向对象编程(Object Oriented Programming)的不足。我们可以通过AOP来实现日志监听,事务管理,权限控制等等。
配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
</beans>
半自动(ProxyFactoryBean)
目标接口UserService.java
public interface UserService {
void addUser();
void updateUser();
void deleteUser();
}
目标类UserServiceImpl.java
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Override
public void addUser() {
System.out.println("addUser...............");
}
@Override
public void updateUser() {
System.out.println("updateUser...............");
}
@Override
public void deleteUser() {
System.out.println("deleteUser...............");
}
}
切面类MyAspect.java
public class MyAspect implements MethodInterceptor{
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation method) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("准备调用方法。。。。。。。。。。");
method.proceed();
System.out.println("调用方法结束。。。。。。。。。。");
return null;
}
}
配置文件applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!-- 目标类 -->
<bean name="userServiceImpl" class="com.hu.service.impl.UserServiceImpl"></bean>
<!-- 切面类 -->
<bean name="myAspect" class="com.hu.aspect.MyAspect"></bean>
<!-- 代理工厂 -->
<bean name="proxyFactory" class="org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean">
<property name="proxyInterfaces" value="com.hu.service.UserService"></property>
<property name="target" ref="userServiceImpl"></property>
<property name="interceptorNames" value="myAspect"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
测试类Demo.java
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
UserService userService = (UserService) context.getBean("proxyFactory");
userService.addUser();
context.close();
}
}
运行结果

切面类MyAspect实现了接口MethodInterceptor,CGLIB代理模式也是使用的该接口。配置文件中的代理工厂ProxyFactoryBean中需要几个属性:
- interfaces : 确定接口
- target : 确定目标类
- interceptorNames : 通知切面类的名称,类型String[],如果设置一个值 value=””
- optimize :强制使用cglib
全自动(aop:config)
aop:advisor
修改配置文件applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!-- 目标类 -->
<bean name="userServiceImpl" class="com.hu.service.impl.UserServiceImpl"></bean>
<!-- 切面类 -->
<bean name="myAspect" class="com.hu.aspect.MyAspect"></bean>
<aop:config proxy-target-class="true">
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(* com.hu.service.UserService.*(..))" id="pointcut"/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="myAspect" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/>
</aop:config>
</beans>
测试类中获取的bean修改为目标bean
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
UserService userService = (UserService) context.getBean("userServiceImpl");
userService.addUser();
context.close();
}
}
运行结果

aop:aspect
配置文件applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!-- 目标类 -->
<bean name="userServiceImpl" class="com.hu.service.impl.UserServiceImpl"></bean>
<!-- 切面类 -->
<bean name="myAspect" class="com.hu.aspect.MyAspect"></bean>
<!-- proxy-target-class="true"表示强制使用cglib代理 -->
<aop:config proxy-target-class="true">
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(* com.hu.service.UserService.*(..))" id="pointcut"/>
<aop:aspect ref="myAspect">
<aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/>
<aop:before method="after" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/>
<aop:before method="around" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans>
修改切面类MyAspect.java
public class MyAspect{
public void before() {
System.out.println("before。。。。。。。。。。");
}
public void after() {
System.out.println("after。。。。。。。。。。");
}
public void around() {
System.out.println("around。。。。。。。。。。");
}
}
运行结果

aop:aspect与aop:advisor的区别
其实,不管是aop:advisor还是aop:aspect最终的实现逻辑是一样的。
- < aop:aspect>:定义切面(切面包括通知和切点)
- < aop:advisor>:定义通知器(通知器跟切面一样,也包括通知和切点)
实现方式不同
< aop:aspect>定义切面时,只需要定义一般的bean就行,而定义< aop:advisor>中引用的通知时,通知必须实现Advice接口(如MethodInterceptor)。
使用场景不同
aop:advisor大多用于事务管理。aop:aspect大多用于日志,缓存。
基于注解
配置文件applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!-- 注解扫描包 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.hu"></context:component-scan>
<!-- 使用AOP注解 -->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy proxy-target-class="true"></aop:aspectj-autoproxy>
</beans>
给目标类UserServiceImpl.java添加注解
@Component
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Override
public void addUser() {
System.out.println("addUser...............");
}
@Override
public void updateUser() {
System.out.println("updateUser...............");
}
@Override
public void deleteUser() {
System.out.println("deleteUser...............");
}
}
定义切面类UserAspect.java
@Aspect
@Component
public class UserAspect {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.hu.service.UserService.*(..))")
public void check() {
//方法体须为空,否则会报错
}
}
定义增强类UserAdvice.java
@Aspect
@Component
public class UserAdvice {
@Before("com.hu.aspect.UserAspect.check()")
public void before() {
System.out.println("before。。。。。。。。。。");
}
@After("com.hu.aspect.UserAspect.check()")
public void after() {
System.out.println("after。。。。。。。。。。");
}
@Around("com.hu.aspect.UserAspect.check()")
public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("around-before。。。。。。。。。。");
joinPoint.proceed();
System.out.println("around-after。。。。。。。。。。");
}
}
运行测试类

定义一个切面类UserAspect,在其中定义一个check方法监听着UserService中的所有方法。再定义增强方法,监听切面类中的check方法。在目标方法被调用时,会带动切面类中的check方法;然后再带动增强类中的方法。若使用了Around注解,则方法体内需要调用ProceedingJoinPoint.proceed()方法,否则会造成目标方法不会被执行。
在定义PointCut的时候,其中的expression值比较复杂。我们可以自定义一个注解,然后监听所有拥有该注解的方法。并且还可通过注解属性设置方法权限。
自定义一个注解MyAnnotation.java
// 注解会在class字节码文件中存在,在运行时可以通过反射获取到
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
// 注解可以被继承
@Inherited
public @interface MyAnnotation {
public String value() default "";
}
给目标方法UserServiceImpl.java添加注解
@Component
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Override
@MyAnnotation(value="normal")
public void addUser() {
System.out.println("addUser...............");
}
@Override
@MyAnnotation(value="admin")
public void updateUser() {
System.out.println("updateUser...............");
}
@Override
@MyAnnotation(value="admin")
public void deleteUser() {
System.out.println("deleteUser...............");
}
}
修改切面类UserAspect.java
@Aspect
@Component
public class UserAspect {
@Pointcut(value="@annotation(com.hu.annotation.MyAnnotation)")
public void check() {
}
}
运行测试类

在实际开发中,Around注解使用的比较多,因为只有它支持ProceedingJoinPoint(可以获取到目标类和目标方法)。可以通过该类获取到当前方法,然后在获取该方法注解中的属性值。从而根据该值判断执行权限,判断该方法是否执行。
修改UserAdvice.java
@Aspect
@Component
public class UserAdvice {
@Around("com.hu.aspect.UserAspect.check()")
public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();
//通过Signature获取到的是代理 并不是原生的
//需要先获取到当前的代理方法,从而获取方法名和参数列表
Method proxyMethod = signature.getMethod();
//获取被代理方法本身(代理方法无法获取到注解)
Method method = joinPoint.getTarget().getClass()
.getDeclaredMethod(proxyMethod.getName(), proxyMethod.getParameterTypes());
MyAnnotation annotation = method.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class);
//假设当前用户权限为 normal
String permission = "normal";
if(permission.equals(annotation.value())) {
System.out.println("准备执行方法............");
joinPoint.proceed();
System.out.println("方法执行完毕............");
}else {
System.out.println("对不起,你没有权限执行" + proxyMethod.getName() + "方法!");
}
}
}
测试类Demo.java
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
UserService userService = (UserService) context.getBean("userServiceImpl");
userService.addUser();
userService.updateUser();
userService.deleteUser();
context.close();
}
}
执行结果
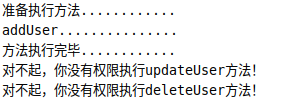
需要注意的是,通过joinPoint.getSignature()获取到的方法是被代理后的方法,被代理后的方法获取不到标注到原方法上的注解。
引入(Introduction)
引入在AspectJ中被称为inter-tye声明,它可以使代理对象实现一个给定的接口用来添加额外的方法或字段。我们首先引入一个新的接口以及接口的实现类,然后再通过@DeclareParents来定义一个引入,其中value表示要引入的目标对象,defaultImpl表示要实现接口的实现类的Class对象。
创建额外接口ExtraService.java
public interface ExtraService {
void deleteAllUser();
}
创建额外接口的实现类ExtraServiceImpl.java
@Component
public class ExtraServiceImpl implements ExtraService {
@Override
public void deleteAllUser() {
System.out.println("deleteAllUser.............");
}
}
修改切面类UserAspect.java
@Aspect
@Component
public class UserAspect {
@Pointcut(value="@annotation(com.hu.annotation.MyAnnotation)")
public void check() {
//方法体须为空,否则会报错
}
//value 表示被代理对象 "+"表示person的所有子类;
//defaultImpl 表示默认需要添加的新的类
@DeclareParents(value="com.hu.service.UserService+",defaultImpl=ExtraServiceImpl.class)
public ExtraService extraService;
}
测试类Demo.java
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
UserService userService = (UserService) context.getBean("userServiceImpl");
userService.addUser();
userService.updateUser();
userService.deleteUser();
ExtraService extraService = (ExtraService) userService;
extraService.deleteAllUser();
context.close();
}
}
运行结果
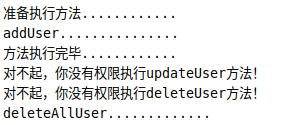
UserService中并没有deleteAllUser方法,却也得到了执行。





